Roses, though beautiful and fragrant, are often plagued by a variety of pests, diseases, and nutritional issues. Effective care and proper treatment ensure your rose garden remains vibrant and healthy all year round.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- Common diseases of roses
- Insect & mite infestations
- Pesticide and fungicide applications
- Use of fertilizers and micronutrients
- Expert tips and dos & don’ts 🚫✅
🦠 Common Diseases of Roses & Their Control
Roses are susceptible to several fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases. Knowing how to identify and manage these is crucial.
1. 🌿 Black Spot (Diplocarpon rosae)
- Symptoms: Circular black spots with yellow margins on leaves
- Effect: Premature leaf drop, weak plant
- Control:
- Remove affected leaves
- Apply Mancozeb 0.25% or Chlorothalonil weekly
- Ensure good air circulation
2. ❄️ Powdery Mildew (Podosphaera pannosa)
- Symptoms: White powdery coating on buds, leaves
- Control:
- Use wettable sulfur or Tridemorph 0.1%
- Spray early morning or late evening
3. 🔥 Downy Mildew
- Symptoms: Purple or dark brown irregular spots on leaves
- Control:
- Remove infected parts
- Apply Metalaxyl + Mancozeb (0.2%)
4. 💧 Rust (Phragmidium spp.)
- Symptoms: Orange pustules on underside of leaves
- Control:
- Apply Sulfur dust or Myclobutanil
- Avoid overhead watering
5. 🧬 Rose Mosaic Virus
- Symptoms: Yellow zig-zag patterns on leaves
- Control:
- No chemical cure
- Destroy infected plants
- Use virus-free stock for planting
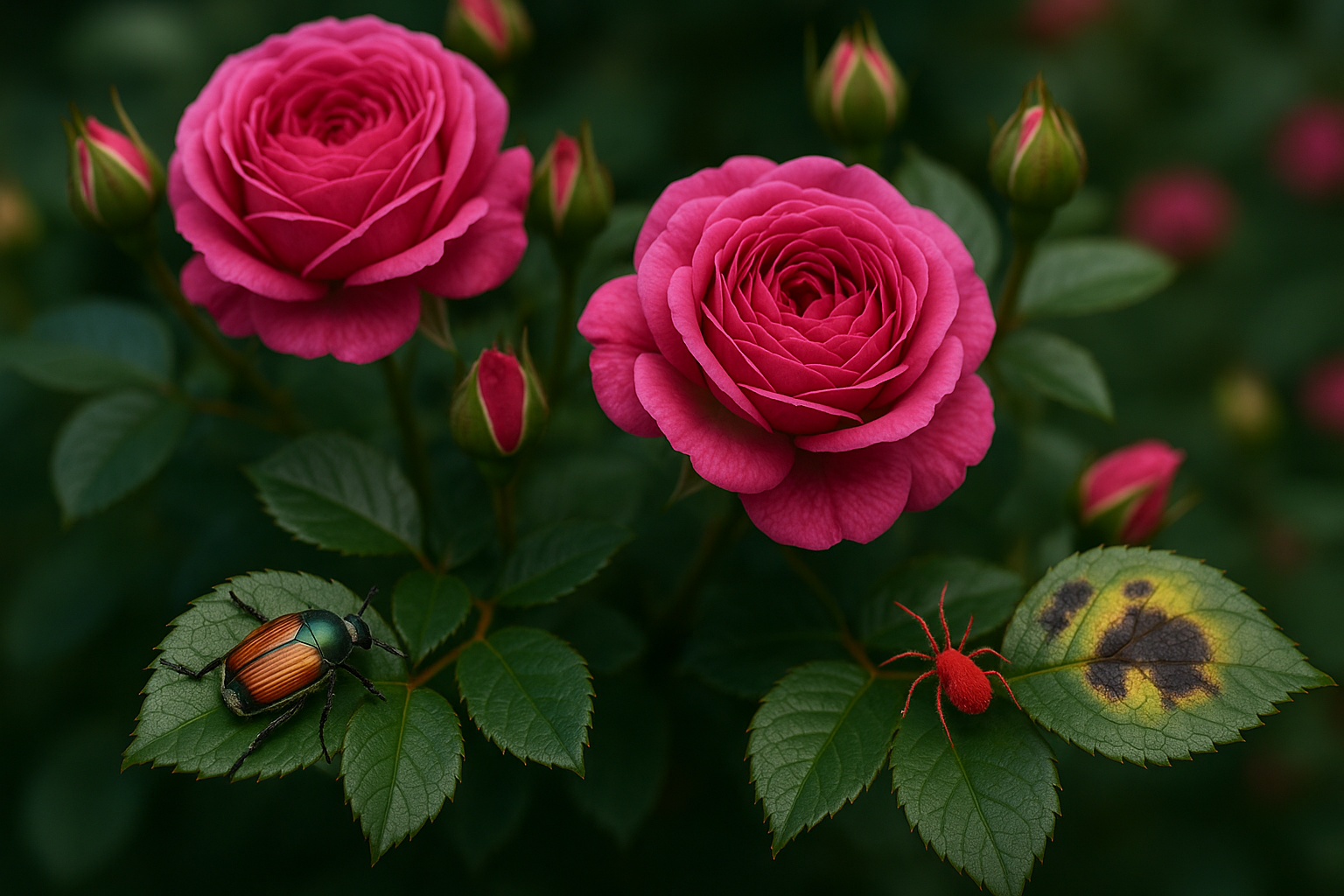
🐞 Common Insect Infestations & Control Measures
Roses attract a variety of pests that can hinder growth and flowering.
1. 🐛 Aphids
- Damage: Suck sap from shoots and buds, causing curling
- Control:
- Spray Neem Oil (3-5 ml/litre) or Imidacloprid 0.3 ml/litre
2. 🦋 Thrips
- Damage: Brown streaks on petals, distorted blooms
- Control:
- Apply Spinosad 2.5% SC (1 ml/litre) or Fipronil 0.3 ml/litre
3. 🐜 Mealybugs
- Damage: Cotton-like clusters on stems and roots
- Control:
- Apply Malathion 50 EC (2 ml/litre) or Chlorpyrifos
4. 🪳 Scale Insects
- Damage: Brown scales on stems and undersides of leaves
- Control:
- Apply Dimethoate 30 EC (2 ml/litre) or Horticultural oil
🕷️ Mites Infestation & Control
Red Spider Mites
- Symptoms: Tiny red dots, webbing, bronzed leaves
- Conditions: Dry, hot climates
- Control Measures:
- Spray Dicofol (2.5 ml/litre) or Abamectin 1.9 EC (0.5 ml/litre)
- Increase humidity around plants
💡 Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Tips
- 👀 Regularly inspect leaves (especially undersides)
- 🍃 Remove and destroy infested plant parts
- 🌼 Use companion plants like garlic or marigold to deter pests
- 🧴 Alternate insecticides to prevent resistance buildup
🌿 Insecticides, Pesticides & Fungicides in Roses
Here’s a helpful table for reference:
| Pest/Disease | Product | Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Imidacloprid | 0.3 ml/litre |
| Thrips | Spinosad | 1 ml/litre |
| Black Spot | Mancozeb | 2 g/litre |
| Powdery Mildew | Sulfur dust | As directed |
| Mites | Abamectin | 0.5 ml/litre |
| Scale Insect | Dimethoate | 2 ml/litre |
🧤 Always wear protective gloves while applying chemicals.
🌾 Use of Fertilizers, PGRs, and Micronutrients
Healthy nutrition boosts immunity and bloom quality.
Recommended Fertilizers:
| Type | When to Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Early spring | Urea |
| Phosphorus (P) | Before blooming | SSP, DAP |
| Potassium (K) | Mid-season | MOP, SOP |
🌸 Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs):
- Gibberellic Acid (GA3) – Enhances stem elongation & flowering
- NAA – Promotes root development
🌟 Micronutrients:
- Zinc, Boron, Iron – Essential for overall health
- Use micronutrient mixture (available as foliar spray)
❗ Dos & Don’ts of Pesticide and Fungicide Use
✅ Do:
- Always follow label instructions 🧪
- Wear gloves, mask, and goggles 🧤
- Apply in early morning or late evening ☀️
- Rotate chemicals to prevent resistance 🔄
❌ Don’t:
- Don’t apply during peak sunlight 🌞
- Don’t mix incompatible chemicals 🧫
- Don’t overuse – may harm beneficial insects 🐝
- Don’t apply just before rainfall 🌧️
❓ FAQs About Rose Pests & Disease Control
Q1: How often should I spray my roses?
A: Ideally, every 7–10 days during active growth or when symptoms are seen.
Q2: Are homemade remedies effective?
A: Yes, neem oil, garlic spray, and soap solutions work for minor infestations.
Q3: Can I grow organic roses?
A: Absolutely! Choose disease-resistant varieties and use organic sprays.
Q4: Why are my rose leaves turning yellow?
A: Could be nutrient deficiency or fungal disease like black spot.
Q5: What is the best time to apply pesticides?
A: Early morning or evening when temperatures are lower.
🌺 Final Thoughts
Caring for roses involves vigilance, but the reward is worth the effort. With the right mix of observation, organic practices, and chemical interventions (when needed), your roses will stay lush, vibrant, and pest-free 🌹✨.









Leave a Reply